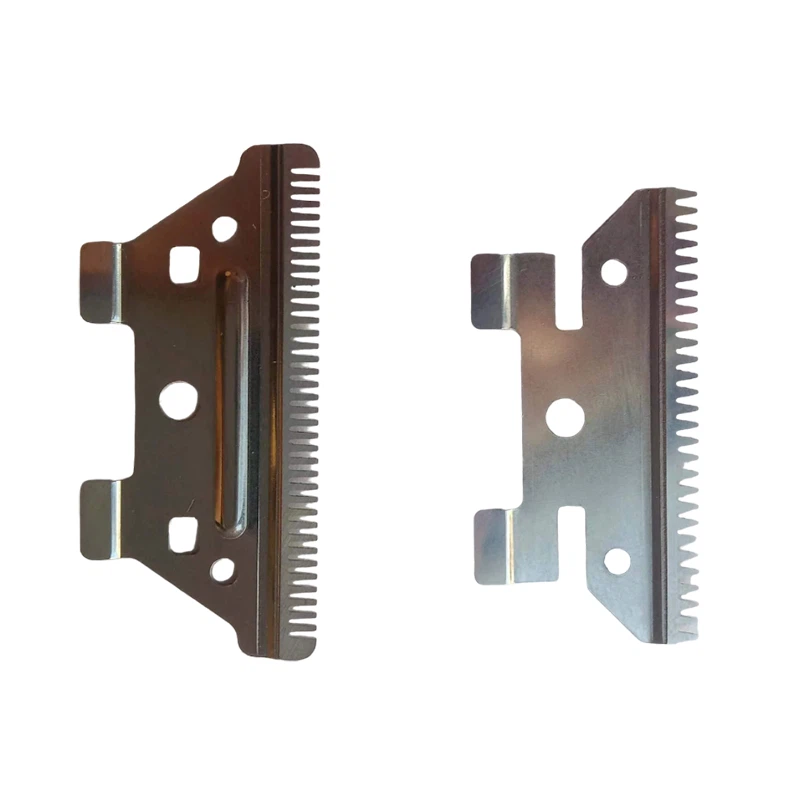
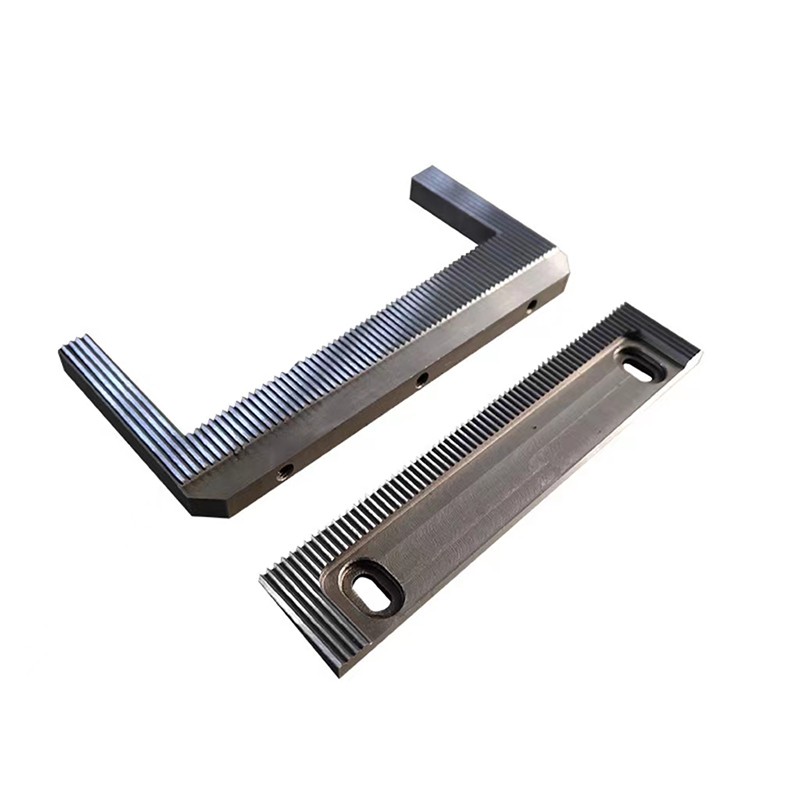
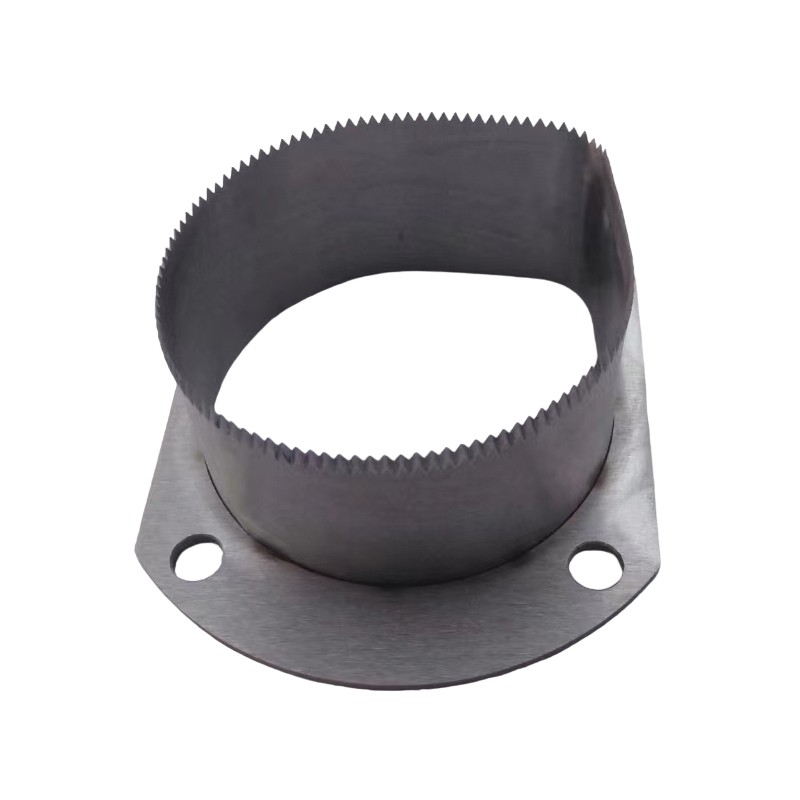
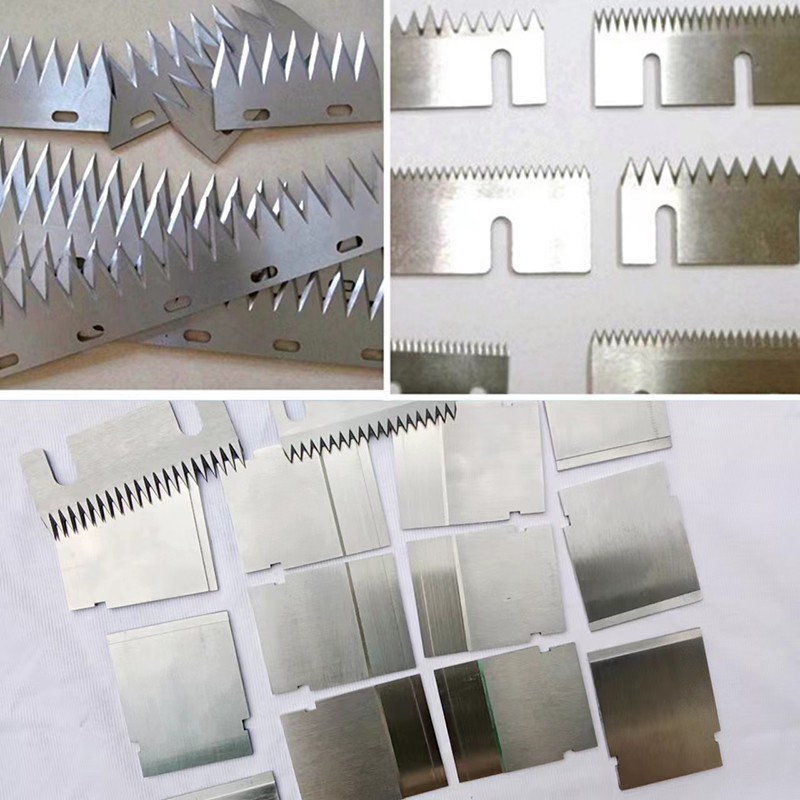
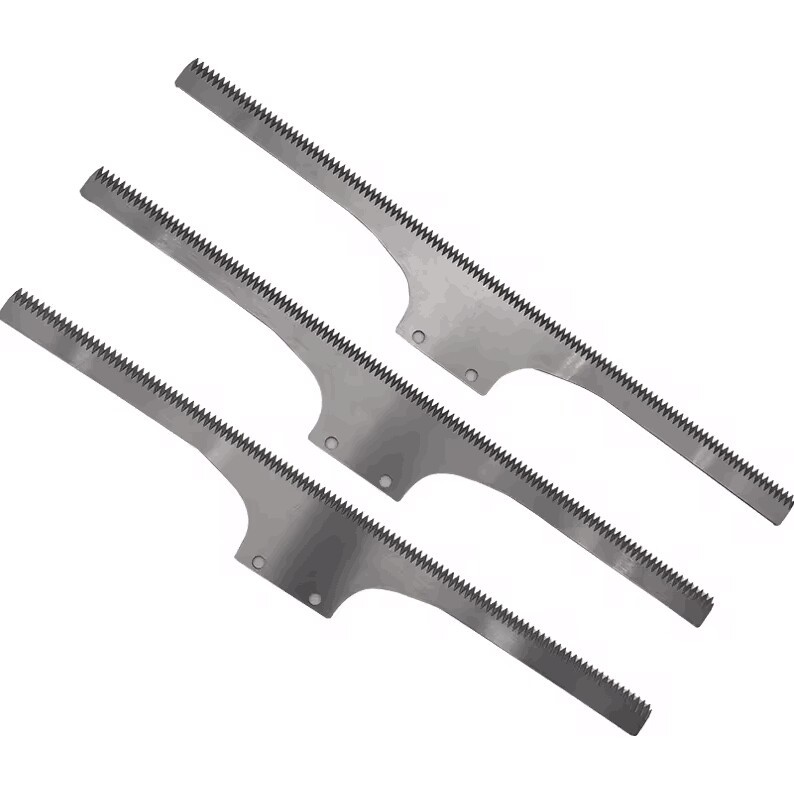
Description
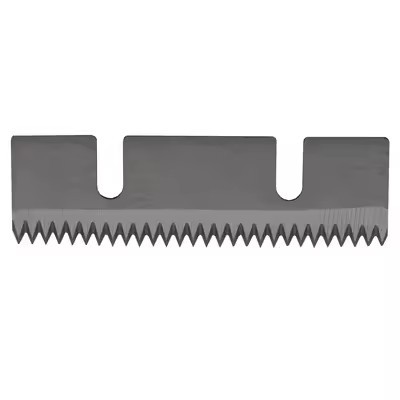
A Toothed Blade is a type of cutting tool or component that features serrated edges or teeth along its cutting edge. These teeth are designed to grip and cut through materials more effectively, especially when dealing with tough or fibrous materials. Toothed blades are commonly used in various applications such as saws, knives, shredders, and cutting tools where a more aggressive cutting action is required. The teeth on the blade help to improve cutting efficiency, reduce binding, and provide a cleaner cut, particularly in materials like wood, plastic, and metal.
Advantages of Toothed Blade
For repeatable precision
The Toothed Blade are capable of making precise cuts quickly and repeatedly with a very good surface finish. These Toothed Blade are very strong and cut through materials effortlessly.
Long life
If you are cutting mild to high carbon steel, we recommend using a cermet tip. Due to its ceramic properties, it is a highly heat resistant blade, but very brittle. If cutting non-ferrous, bearings, tool steels, or stainless steels, we recommend using a coated tungsten carbide tip. Tungsten is more impact resistant, still has high heat resistance (less than cermet), and lasts longer.
Coatings for longer life
Toothed Blade are available with coatings that extend the life of the blade. It creates less resistance and friction when cutting through the material, resulting in less material loss and a smoother finish.
Increased productivity
If you don't want to waste money on saw blades that have a short life, a cermet tip is definitely worth the investment. Typically, they stay sharper longer. Reducing the number of blade changes keeps the saw running and the operator can focus on more important tasks.
Less downtime
Did you know that a cermet tip can last for thousands of cuts? Not only do you gain an advantage in cutting time, you also save time changing saw blades by not having to change them as often as your competitors. Let them change the saw blades while your production work is going on.
High Cut Rate, Low Energy Consumption, Low Material Loss
Longer life and faster cutting speeds are the main reasons why shops switch to round blades. Carbide blades are sharper right out of the gate and stay sharper much more than steel blades due to their resistance to wear and heat. A sharper edge means less chipping and shattering at higher feed rates. You won't have to change blades as often, saving you time and money in the long run.
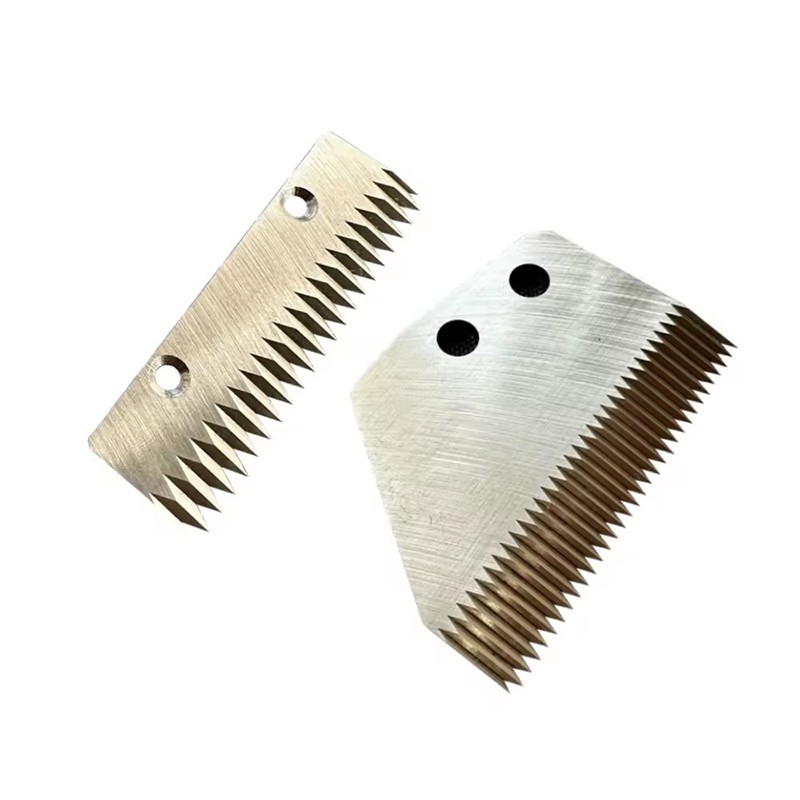
The sealing machine blade is a key component widely used in the packaging field. It is made of high-quality steel and has excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and cutting performance. The sealing machine blade not only can easily cut various packaging materials, such as cartons, foam boards and plastic sheets, but also can be switched and adjusted according to different needs, with high flexibility.
Charter machine blade is a common metal cutting tool, mainly used for cutting and cutting materials in the feeding machine equipment. This type of blade has a simple structure, is easy to install and replace, greatly improving cutting efficiency and accuracy.
Jelly machine blades are indispensable cutting tools on jelly production lines. They are made of high-strength stainless steel, with a beautiful appearance and reliable quality. The design of the blade is flexible and can be adjusted according to the hardness and shape of different jellies, ensuring that each piece of jelly can be cut evenly and neatly.
Automatic packaging blades are state-of-the-art cutting tools that play a pivotal role in the packaging industry. These blades are designed to provide efficient and accurate results, while also reducing the risk of errors and injuries. They are specifically designed to cut through a wide range of packaging materials including tapes, films, foils, and papers.
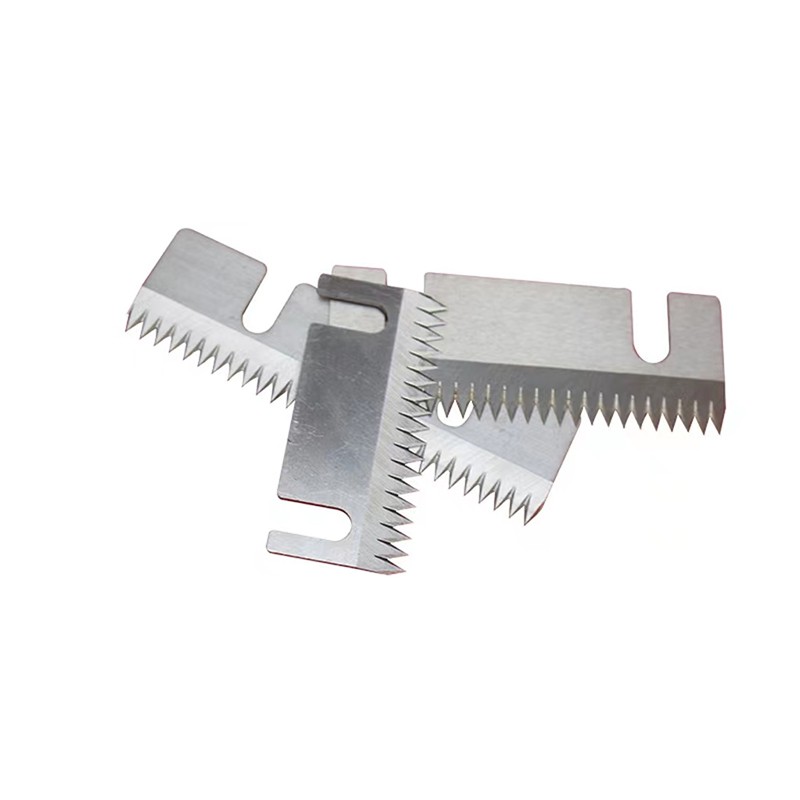
Non-standard blades refer to blades that are specifically designed and manufactured for a particular use, rather than being standard, off-the-shelf items. These blades are tailor-made to suit the specific needs of a particular application. They are used in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and manufacturing.
Dotted paper cutting blade is a cutting tool suitable for cutting items such as dot matrix paper, greeting cards, envelopes, etc. Its blade is designed with many small serrated blades, which can cut high-quality lattice lines in a short time, making the cutting effect more beautiful.
Filling Machine Tooth Cutting Blade
Filling machine tool cutting blade is a cutting blade used for filling machines. It is widely used in the production process of industries such as food, medicine, cosmetics, etc., to cut materials and complete the sealing of bottles or bags. Its design ensures precise cutting and sealing during the filling process, ensuring product quality and hygiene standards.
Packaging machine blades are widely used in the process flow of various sewage treatment plants to promote the mixing of wastewater containing suspended solids, diluted mud, industrial process liquids, etc.
T Type Packaging Machine Blade
The T type packaging machine blade is a high-quality and powerful tool that can greatly improve the efficiency of the packaging machine. It is mainly used for cutting and cutting products in various packaging machines, suitable for various fluid packaging, filling and sealing, such as packaging in the fields of pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, etc.
Why Choose Us
Factory
The company is a professional industrial cutting tool production and processing enterprise. The company team has 15 years of industry experience. Through years of continuous accumulation and exploration, it has successfully completed technological transformation.
High-quality service
We insist on returning the support and love of our customers and friends from all parties with stable, reliable, economical, durable and high-quality products.
Customized service
Our team of experts will work closely with you to understand your needs and provide tailor-made solutions to meet your expectations.
Competitive price
We are confident in the quality of our products and are willing to provide you with long-term technical service support.
Types of Toothed Blade




Miter saw
This cutting tool mimics a hand saw, making it ideal for performing trim work and jobs that require precise measurements. A miter saw blade rotates in a clockwise direction. When installing a new blade, make sure the teeth are pointing downward to enable a clean cut through the workpiece. Upward-facing teeth can cause a severe injury to the operator.
Table saw
Table saws are typically the best choice for making rip cuts or when preparing a large volume of identically sized pieces. A challenge when determining the right direction for table saw teeth is that the saw conceals most of the blade, making it hard to see the teeth. Like miter saws, table saw blades rotate clockwise, meaning the teeth should be pointing down.
Circular saw
Circular saws are the most commonly used power saw. They can accommodate a variety of blades for cutting wood and other materials such as masonry, plastic and metal. The proper direction of the blade's teeth depends on the type and model of the saw. Be sure to check the arrows on the blade to determine the rotation.
Hand saw
If you're using a non-motorized hand saw for cutting wood, the blade's teeth should always point in a downward direction.
Toothed Blade:Band saw blades have 5 different tooth figurations
Regular tooth saw blades
The teeth are evenly spaced along the saw blade. Where one tooth ends, another tooth begins. Regular tooth saws are commonly used. They are straight teeth with deep grooves. These types of saws are used for both contouring and cutting. It is a type of general purpose saw blade for thin metals.
Hook tooth saw blades
The hook-like teeth are widely spaced and inclined at 10°. Hook-type saw blades with large teeth and deep grooves are suitable for rough and long cuts. Used for hard non-ferrous alloys.
Wavy toothed saw blades
The teeth are not aligned perfectly straight. In this saw, right and left angled tooth groups come together. Suitable for cutting thin sheets, pipes and metals.
Variable tooth saw blades
In this type, teeth of different sizes and settings come together. Variable angles and grooves reduce vibration. For smooth and fast cuts, this saw is preferred for cutting bevels.
Skip-tooth saw blades
In the skipping tooth figuration, there is a gap next to one tooth, then there is the other tooth. Suitable for non-ferrous metals. This gap prevents the saw from clogging; It helps to clean the burrs and cut the saw faster. It becomes a little difficult to obtain a smooth surface with this type of saw teeth.
Here Are Some Terms and Considerations to Know When Choosing a Toothed Blade
Applications
You need to know which saw blade you are going to use and what material you are going to cut. Different circular saws and materials require (or perform best) with a blade optimized for that operation. There are universal blades that can handle different materials, but if you know you will probably only (or primarily) cut one type, buy a blade optimized for that type.
Number of teeth
The number of teeth in a blade determines its cutting action. More teeth result in a smoother cut, and fewer teeth result in more material removal by the blade. Crosscut blades have more teeth for smoother cuts along the grain of the material, while slitting blades have fewer teeth and are optimized to cut with the grain, removing more material.
Tooth guillotine
The tooth gullet refers to the space between each tooth on the blade. The wider the gullet, the more material fragments are cut.
Tooth configuration
The shape of a blade's teeth also determines its performance. Teeth are configured to optimize crosscutting, ripping, and processing certain materials, such as laminate, MDF, etc. Some common tooth types include Flat Top (FT), optimized for ripping, Alternate Top Bevel (ATB), optimized for crosscutting, and Combination Tooth (CT), which includes both tooth types and is designed for general purpose cutting.
Tooth angle
The tooth angle (or hook angle) refers to the angle of the tooth relative to the centerline of the tooth edge. A tooth edge with a "positive hook angle" means the tooth is tilted forward to a certain degree. A "negative hook angle" means the tooth is tilted backward, in the opposite direction of the tooth edge rotation. The more positive the angle of the tooth edge, the sharper the tooth edge.
Components of Toothed Blade
Bore
The bore of the circular saw blade is the center circle that allows the blade to be attached to the saw via the saw's arbor (the shaft that allows the blade to be secured in position and locked into place).
Kerf
Refers to the thickness of the slot which the saw blade will cut. It is often used as well to define the thickness of the blade itself, or at least the widest point of the blade, as this will define the width of the cut made.
Teeth
The outside points of a blade that do the work cutting the material. There are many different types of teeth that give the user a different type of cut. Generally, the more teeth the blade has the smoother the cut will be, and likewise, the fewer teeth the blade has will cause the blade to remove more material giving a rougher cut.
Gullet
The curved area at the base of the tooth. The tooth tip to the bottom of the gullet is the gullet depth.
Expansion slot
Used primarily on larger diameter blades and functions to create an outlet for heat buildup created during cutting. A steel blade will heat up to a point where the heat is great
Shoulder
The part of the blade body directly behind each tooth that provides support for each tooth. The shoulder's major function is to provide strength and support to the tip of the tooth. A well designed blade allows the shoulder to provide extra strength and helps guide the tip through the material the operator is cutting.
Hook tooth angle
The amount of lean to the blades teeth, and the angle the teeth will engage with the material being cut.
Negative hook angle
Negative angles are blade teeth that have a backward lean. Negative hook angle blades are more appropriate for cross cutting cuts, and are better suited for plywood and non-wood materials such as plastics as well as metal.
Positive hook angle
In contrast to negative hook angle, positive hook angle refers to blade teeth that have a forward lean. Positive hook angles are generally used on rip blades to help pull the wood into the blade. For harder materials, the angle needs to be a smaller degree with less steepness. The higher the value the angle goes, corresponds to softer materials.
Crosscut
Cuts that run across, perpendicular, the grain of the material such as wood.
Rip cut
Cuts that run along the grain, parallel, of the material such as wood.
Rake
Another word for hook angle. The rake of the blades teeth affects the tendency of material to move during cutting. Positive rake helps move the material 'into' the blade, in other words, helps the blade self feed. A negative rake is less aggressive and does not help force the material towards the blade.
Material of Toothed Blade
Stainless steel and specialty alloys
These blades are particularly effective when cutting stainless steel and specialty alloys often used in aerospace, automotive, and other specialized industries.
Metalworking
In metalworking shops, toothed cutters are invaluable due to their ability to accurately and consistently cut a wide range of metals.
Structural steel
The durability and heat resistance of toothed cutters make them a top choice for cutting structural steel beams and profiles.
Tube cutting
Toothed cutter blades are ideal for cleanly and accurately cutting metal tubing, meeting the high quality standards required in construction and manufacturing.
Tool and die manufacturing
The wear resistance of toothed cutters makes them ideal for forming and cutting metal in tool and die production, ensuring longer life for these important components.
How to Sharpen the Toothed Blade
Secure the saw in place
Before you begin sharpening, make sure the saw is securely secured in place with a vise. This ensures stability and prevents the saw from moving during the sharpening process.
Choose the right angle
Find the existing angle of the tooth edge and use that angle. If you have difficulty, you can use a special tooth edge sharpener to maintain the correct angle.
Sharpening the toothed blade
Place the saw file or sharpening steel in the first tooth edge and move it away from you. Use smooth, even motions and apply moderate pressure. Sharpen each tooth edge until the file or sharpening steel covers the entire length of the saw blade.
Work in one direction
Sharpen the saw blade in one direction, preferably away from you. This ensures consistent, sharp results.
Repeat on the other side
Turn the saw around and repeat the process on the other side of the blade. Make sure to give each tooth edge the same attention.
Check the toothed blade
After sharpening, inspect the blade to check that the toothed blade are evenly sharpened. There should be no burrs or blemishes.
How to Maintain Toothed Blade
Clean regularly
After each use, clean the toothed blade and remove any metal shards or debris stuck to the teeth, as these particles can cause corrosion or dullness over time. Use a soft brush and, if necessary, mild soap and water for cleaning. Make sure the toothed blade is dry before storing it.
Lubrication
Applying a light lubricant to the toothed blade can prevent rust, especially when working in high humidity environments. Lubrication also reduces the strain on the saw and toothed blade, making the cutting process smoother.
Storage
When not in use, store the toothed blade in a dry, mild environment to prevent humidity from causing rust or warping. Hanging the toothed blade vertically or in its original packaging will also help preserve its shape.
Inspection
Regularly inspect the toothed blade for wear, damage, or dullness. Catching problems early can prevent further damage and maintain the quality of your cuts. If you notice missing or damaged teeth, you may need to replace the toothed blade.
Sharpening
Depending on the toothed blade type, professional resharpening can significantly extend its life. For example, you can restore the edge of carbide and high-speed steel toothed blades by sharpening. However, sharpening a knife can be a little difficult for beginners, so let a professional handle it.
Our Factory
Ganzhou Big Brother Cutting Tools Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and processor of industrial cutting tools. The company team has 15 years of industry experience and has successfully completed technological transformation through years of continuous accumulation and exploration.Also skilled in researching and producing non-standard cutting tools, molds, etc The main products include: packaging machine knives, non-standard blades, industrial knives, food machine knives, woodworking planers, alloy blades, precision knife molds, shredder knives, agricultural machinery knives, and various mechanical cutting tools for mass production and non-standard customization.

FAQ
Q: What is a toothed blade?
Q: What are toothed blades made of?
Q: How are the teeth of a toothed blade formed?
Q: What is the significance of the tooth count on a toothed blade?
Q: What are the different types of tooth configurations?
Q: How does the blade's kerf affect its performance?
Q: What is the difference between a carbide-tipped blade and a solid carbide blade?
Q: Can toothed blades be sharpened?
Q: What is the importance of blade tension in a toothed blade?
Q: What is blade drift?
Q: How does the blade diameter affect its performance?
Q: What is the significance of blade thickness in a toothed blade?
Q: How does blade material affect the type of materials it can cut?
Q: What is the role of blade tooth angle in cutting performance?
Q: How does the blade's arbor size affect its compatibility with a saw?
Q: What safety measures should be taken when using toothed blades?
Q: How does the blade's cutting speed affect its performance?
Q: What maintenance is required for toothed blades?
Q: What is the lifespan of a toothed blade?
Q: How can I determine the right toothed blade for my application?